As Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems grow in complexity and scope, managing end-to-end workflows, spanning data ingestion to model deployment, has become increasingly laborious and error prone. Traditionally, teams of data engineers, data scientists, MLOps professionals, and DevOps engineers have collaborated to design, build, and maintain these workflows. However, this manual approach often leads to inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and prolonged development cycles.
Enter autonomous agents, intelligent software entities capable of independently perceiving tasks, making decisions, and executing operations. These agents can optimize, automate, and scale AI workflows with minimal human supervision. As AI-driven tools evolve, autonomous agents are transforming the way we build, manage, and refine AI systems.
This article explores how AI workflows with autonomous agents integrate, enhancing productivity, adaptability, and performance across the board.
What Are Autonomous Agents?
An autonomous agent is a software system designed to operate independently within a given environment. These agents can perceive their surroundings, reason about goals, make decisions, and take actions without requiring continuous human oversight.
Key traits of autonomous agents include:
- Autonomy: Operate independently
- Perception: Understand the state of the system or environment
- Decision-making: Evaluate options and select actions
- Adaptability: Learn from outcomes and modify behavior
In the context of AI workflows, autonomous agents can manage tasks such as data ingestion, feature engineering, model training, hyperparameter tuning, deployment, and monitoring. By intelligently orchestrating these processes, agents reduce manual labor, accelerate iteration cycles, and improve overall system robustness.
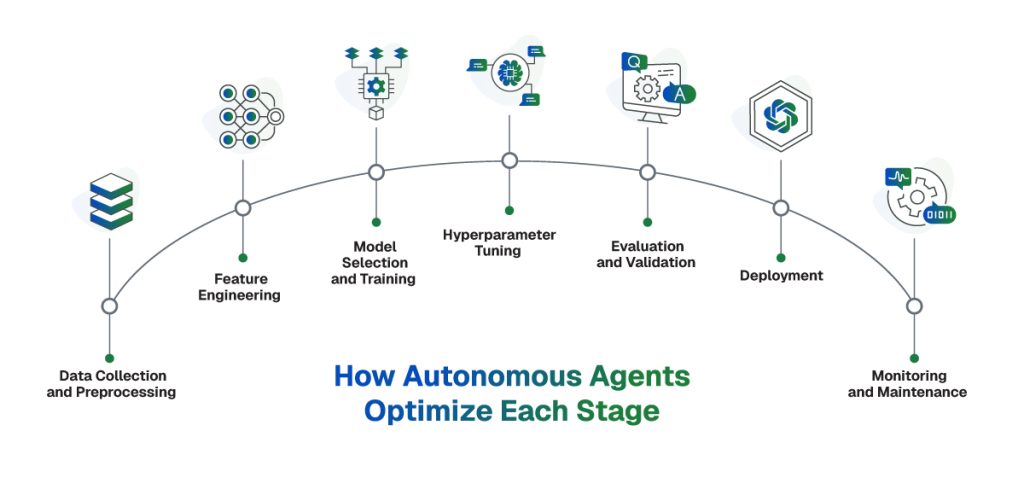
Anatomy of an AI Workflow
To understand where and how autonomous agents add value, let’s first examine the key components of a typical AI/ML workflow:
- Data Collection and Ingestion
Collecting raw data from sources like APIs, sensors, logs, or databases.
- Data Cleaning and Preprocessing
Handling missing values, data normalization, and outlier detection.
- Feature Engineering
Creating meaningful input variables that improve model performance.
- Model Selection and Training
Choosing algorithms, defining architectures, and training models.
- Hyperparameter Tuning
Optimizing model parameters for better performance.
- Evaluation and Validation
Assessing accuracy, fairness, robustness, and generalization.
- Deployment
Packaging, versioning, and serving models in production environments.
- Monitoring and Maintenance
Tracking performance, retraining models, and managing drift.
- Feedback Loops and Retraining
Incorporating new data and results into the system for continuous learning.
Each stage may involve complex dependencies, manual triggers, and decisions that are ripe for automation through autonomous agents.
How Autonomous Agents Optimize Each Stage
Data Collection and Preprocessing
Data preparation is one of the most time-consuming steps in AI workflows. Autonomous agents can connect to APIs, validate schema, detect anomalies, and trigger preprocessing tasks like normalization or enrichment. This ensures models are trained on reliable, high-quality data without heavy manual intervention.
Agents can automate:
- Connecting to data sources
- Verifying data quality and schema
- Flagging anomalies or inconsistencies
- Initiating cleaning and preprocessing scripts
2. Feature Engineering
Feature engineering often requires deep domain expertise. Agents help by analyzing datasets, identifying correlations, generating new features, and managing feature stores for reuse across projects. By automating this process, they reduce effort while improving model interpretability and accuracy.
Agents use statistical and semantic reasoning to:
- Recommend new features
- Evaluate feature importance
- Remove multicollinearity
- Manage feature stores for reusability
3. Model Selection and Training
Testing multiple algorithms and architectures can be computationally expensive. Agents orchestrate parallel experiments, stop underperforming models early, and leverage AutoML to streamline selection. This accelerates experimentation while focusing resources on the most promising candidates.
Agents orchestrate training tasks:
- Test multiple model architectures (e.g., via AutoML)
- Optimize training schedules
- Choose between classical ML, deep learning, or hybrid models
4. Hyperparameter Tuning
Hyperparameter tuning is usually trial and error, but agents can intelligently search parameter spaces using Bayesian optimization or reinforcement learning. They adjust settings dynamically during training, leading to faster convergence and reduced compute costs.
Agents can:
- Efficiently search hyperparameter spaces
- Adjust batch sizes, learning rates, or regularization parameters on the fly
- Handle multi-objective optimization (e.g., accuracy vs. latency)
5. Evaluation and Validation
Model evaluation requires more than accuracy checks. Agents can run automated pipelines to assess robustness, fairness, and bias, while generating explainability reports for stakeholders. If thresholds are not met, they can flag models for retraining or rejection.
Agents:
- Build automated evaluation pipelines
- Conduct fairness, bias, and robustness checks
- Generate performance dashboards and reports
6. Deployment
Deployment is often complex and risky. Agents automate packaging, containerization, and rollout with tools like Docker or Kubernetes, and perform A/B testing to minimize errors. They can also trigger rollbacks if production metrics fall below acceptable levels.
Agents assist with:
- Containerizing models using Docker or OCI standards
- Deploying models via Kubernetes or serverless frameworks
- Validating staging environments and performing A/B tests
7. Monitoring and Maintenance
Models need continuous monitoring after deployment. Agents track real-time metrics, detect drift, and trigger retraining pipelines when necessary. They also optimize infrastructure resources, ensuring AI systems stay adaptive and cost-effective.
Agents:
- Continuously track model performance
- Detect drift in data distributions or prediction accuracy
- Retrain models as needed
Benefits of Using Autonomous Agents
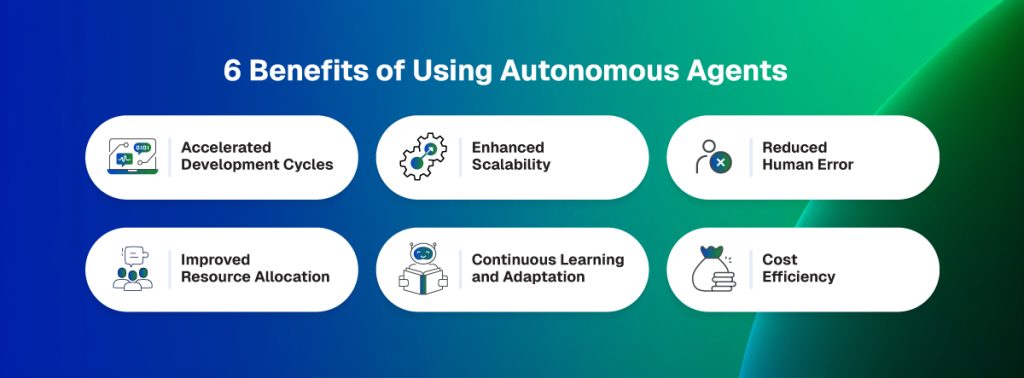
- Accelerated Development Cycles
By automating repetitive tasks like data preprocessing, hyperparameter tuning, and model evaluation, autonomous agents significantly shorten the time required to move from concept to production. This allows teams to iterate faster and focus more on innovation rather than manual operations.
- Enhanced Scalability
Managing hundreds of datasets and models can overwhelm traditional workflows. Autonomous agents handle these tasks in parallel, orchestrating large-scale processes without human bottlenecks, making it easier to scale AI across enterprise-level applications.
- Reduced Human Error
Manual execution of complex workflows often leads to mistakes that affect performance and reliability. Autonomous agents follow defined logic consistently, minimizing errors and ensuring workflows run with greater accuracy and stability.
- Improved Resource Allocation
Agents can dynamically assign compute and storage resources based on workload demands and model performance. This intelligent allocation avoids waste, reduces costs, and ensures high-priority tasks receive the resources they need.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Unlike static systems, autonomous agents can detect changing data patterns and retrain models automatically. This continuous adaptation ensures AI systems remain relevant, accurate, and aligned with evolving environments or business needs.
- Cost Efficiency
By reducing manual labor, preventing workflow errors, and optimizing infrastructure usage, autonomous agents drive significant cost savings. Organizations benefit from both lower operational expenses and higher returns on AI investments.
Conclusion
Autonomous agents are transforming the AI landscape, not by replacing humans, but by enhancing their capabilities. By integrating these agents into AI workflows, organizations can accelerate development, minimize operational friction, and enable continuous learning systems that evolve on their own.
As the ecosystem of tools supporting autonomous agents continues to mature, we can expect a paradigm shift: from static, manually triggered pipelines to dynamic, intelligent, self-improving AI systems.
Whether you’re building models for healthcare, finance, retail, or robotics, adopting autonomous agents isn’t just a technical upgrade, it’s a strategic imperative for the future of AI.
Intelligent Automation, Powered by Heliosz.AI
Supercharge your AI workflows with Heliosz Autonomous Agents. From data to deployment, let intelligent automation streamline your processes, reduce errors, and unlock scalability.
Transform your business workflows today with Heliosz.